Reviewing Your Linux Hosting Resource Allocation and Usage in cPanel
Introduction
Understanding and managing your resource allocation and usage on cPanel is crucial for optimizing your website's performance. This guide will help you review your Linux hosting resources, such as storage, bandwidth, and other key parameters on cPanel.
Section 1: Accessing cPanel
Login to cPanel: To start, you need to access your cPanel account. You can do this by appending '/cpanel' to your domain name (e.g., https://<your-domain-name>/cpanel) or via the link provided by our Support Team. Use your username and password to log in, as illustrated in Figure 1 below.

You will land on the dashboard page upon successful login, as illustrated in Figure 2 below.
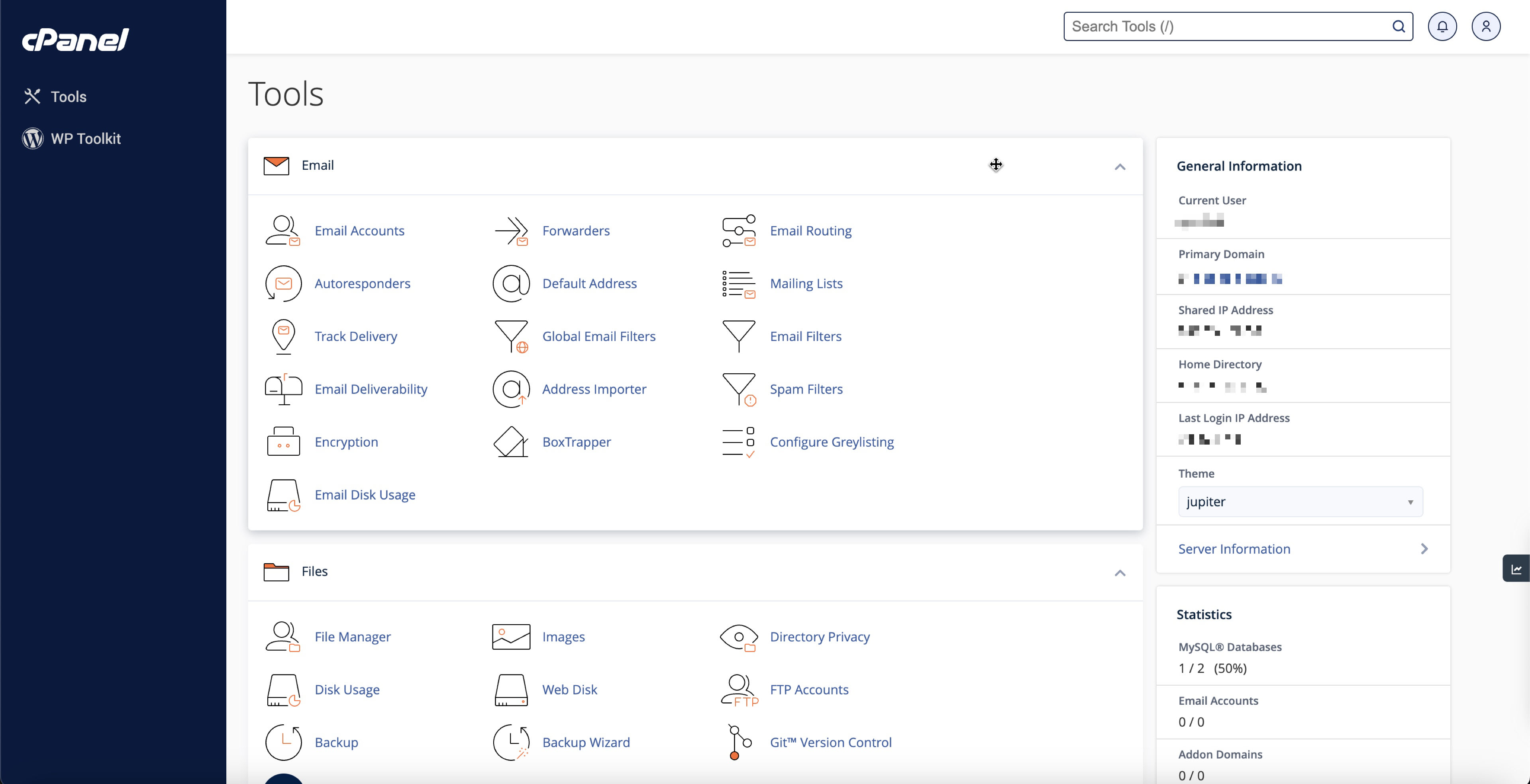
Section 2: Reviewing Storage Usage
The "Disk Usage" section provides an overview of how much storage you're utilizing. Go to the Files section in the dashboard and click on the Disk Usage link, as illustrated in Figure 3 below.
You will land on the page after clicking the disk usage link, as shown in Figure 4 below.
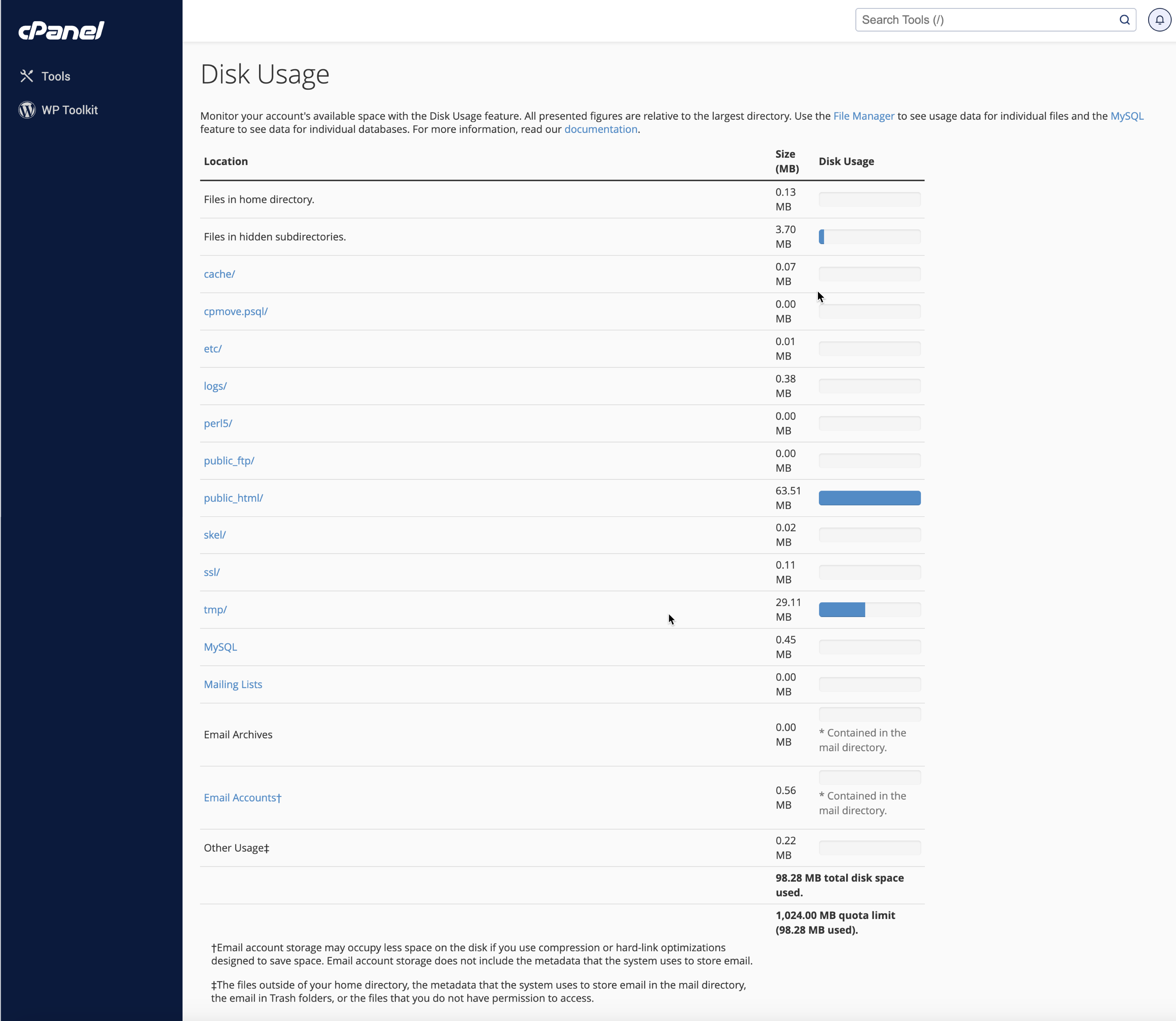
On the screen, you will find the disk usage of the root folders of your hosting account, as illustrated in Figure 4 above.
To view individual subfolders' disk usage, scroll down as illustrated in Figure 5 below.
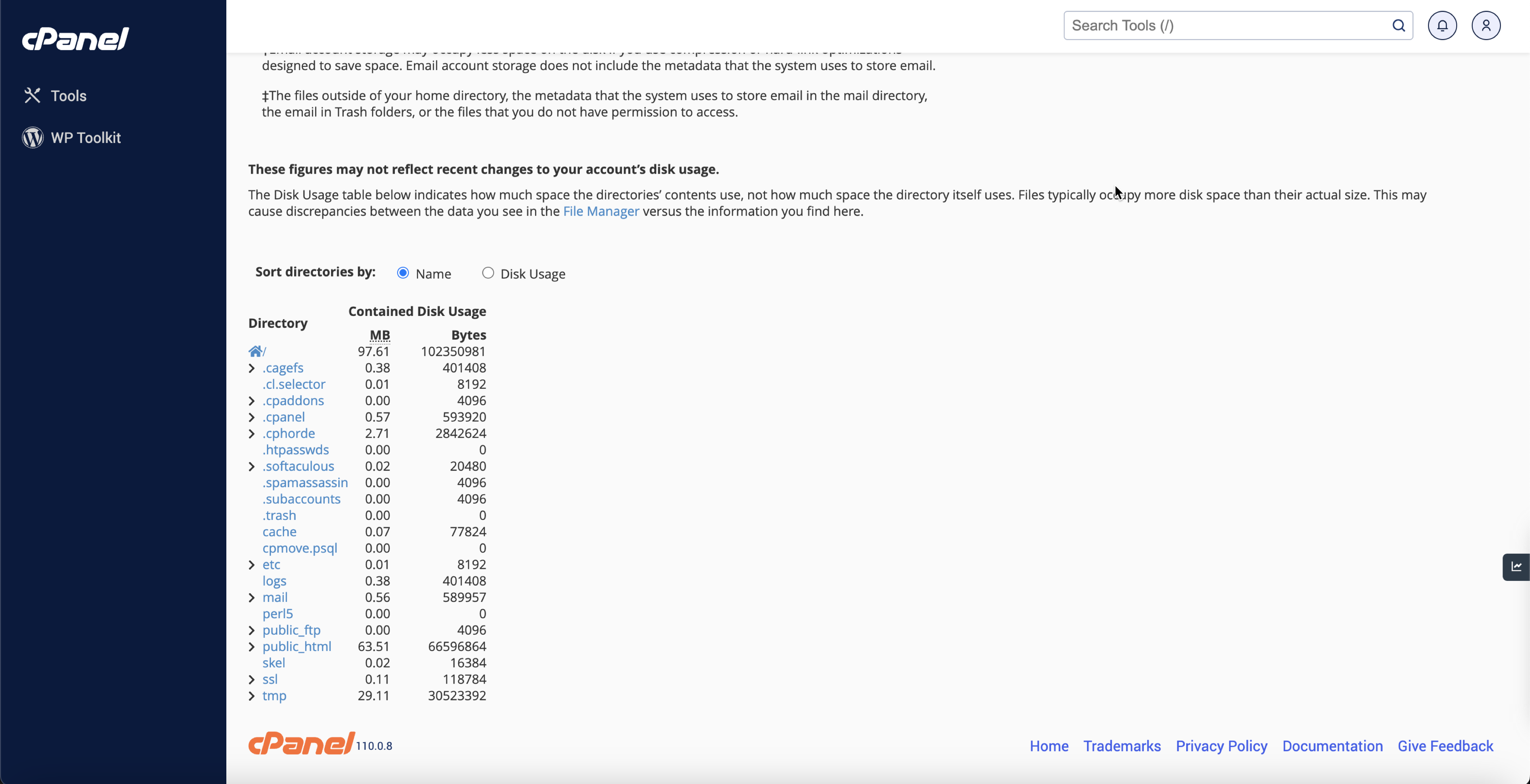
Here, you'll see a comprehensive list of directories, along with the amount of disk space each one is occupying. This breakdown helps identify which directories consume most of your storage.
Section 3: Evaluating Bandwidth Usage
The "Bandwidth" tool in cPanel gives insights into data transfer over various time frames. Go to the Metrics section in the dashboard and click on the Bandwidth link, as illustrated in Figure 6 below.
After clicking the bandwidth link, you will land on the page, as shown in Figure 7 below.
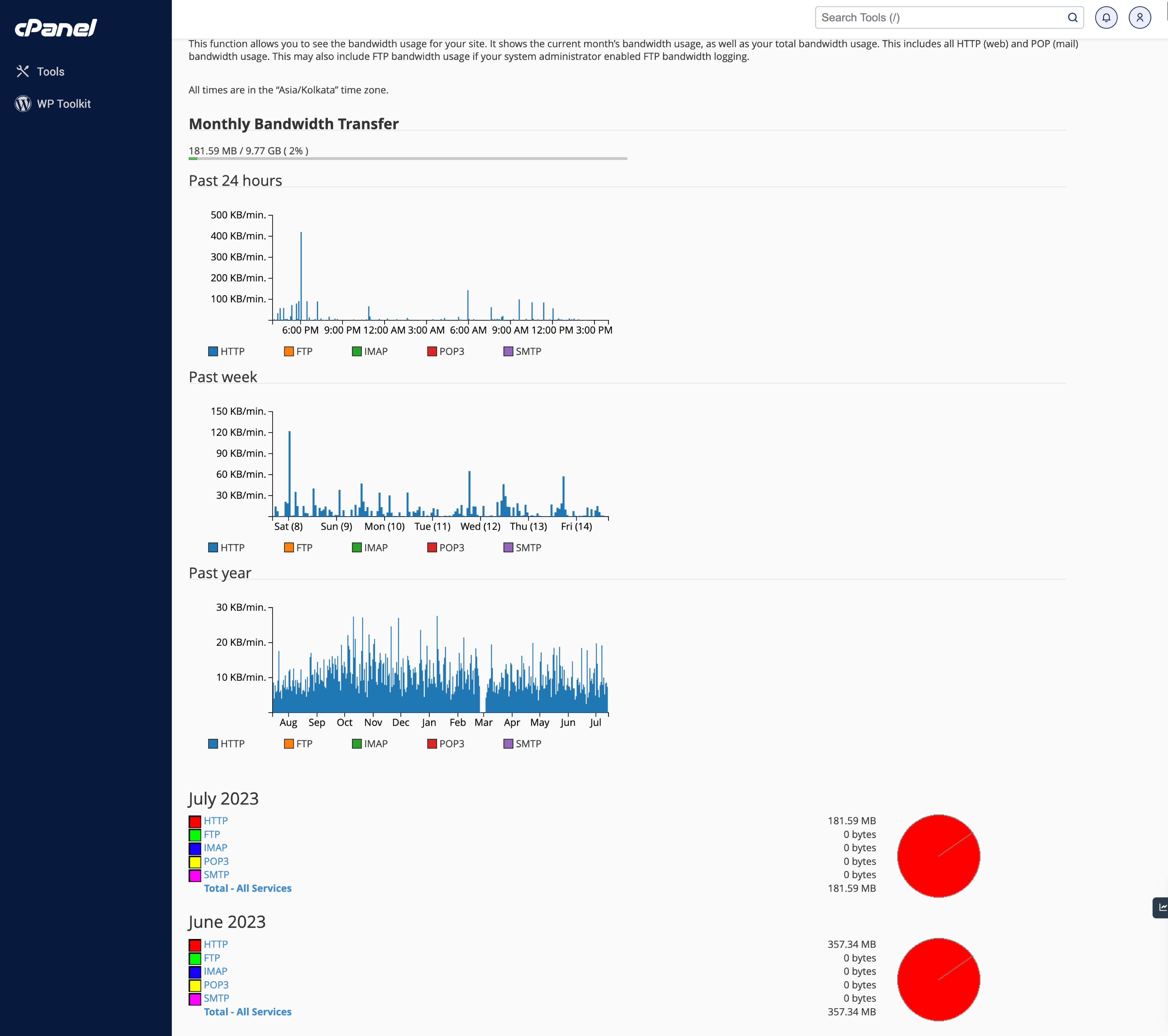
On this page, you can find all the bandwidth usage in different segments like the Past 24 hours, Past week, and Past year and detail individual month-wise data as illustrated in Figure 7 above.
Here, you can see the total bandwidth used by your website over the past day, week, and month. You can view the data in graphical form to better understand your website's traffic trends.
Section 4: Checking Email Disk Usage
If you're using cPanel's built-in email server (please check this correctly), monitoring its storage usage is essential too. On the cPanel main page, go to "Email Disk Usage" under the "Email" section, as illustrated in Figure 8 below.

Review Email Usage: This page shows a list of your email accounts and the disk space each uses, as illustrated in Figure 9 below.
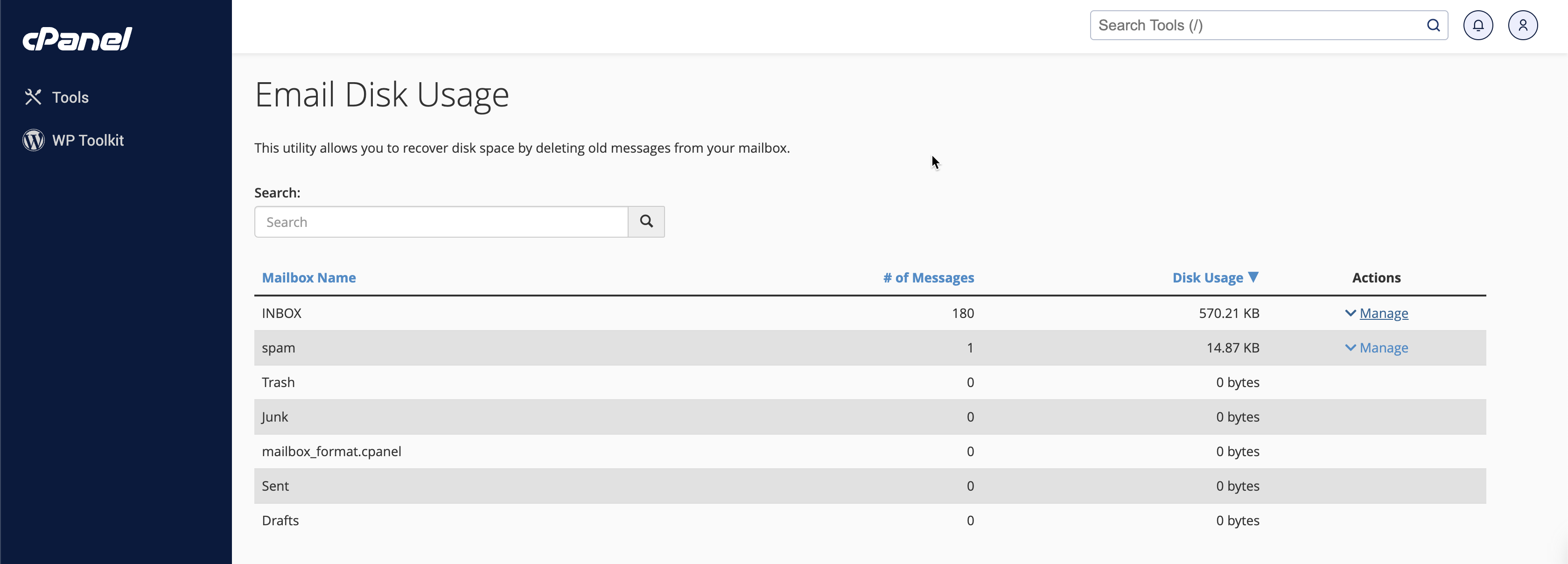
Delete Email Usage: To delete the file from a particular email ID, click the Manage link on the right under the action section, as illustrated in Figure 10 below.
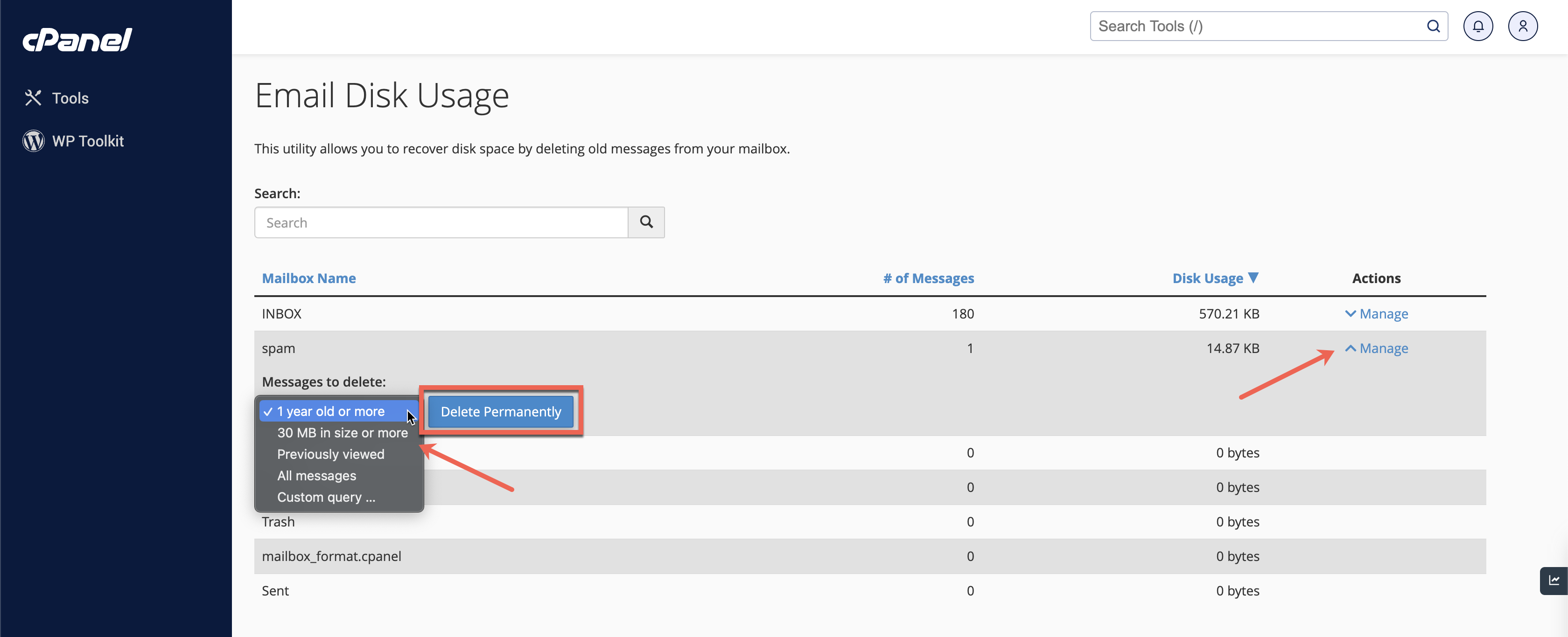
Click on the Message to Delete drop menu, select the option, and click the Delete Permanently button, as illustrated in Figure 10 above.
Section 5: Reviewing CPU and Concurrent Connection Usage
To understand your server's performance, check CPU usage and the number of concurrent connections by clicking on the Server Information link from the cPanel dashboard, as illustrated in Figure 11 below.
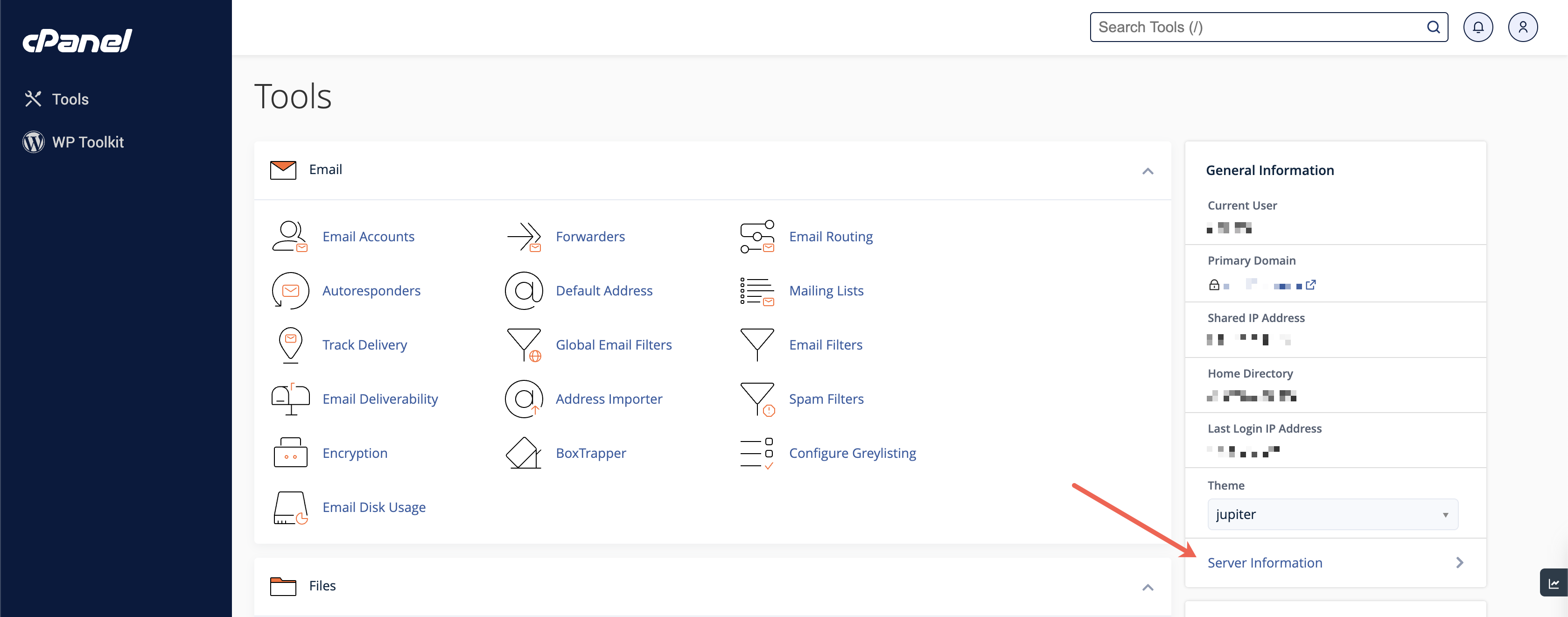
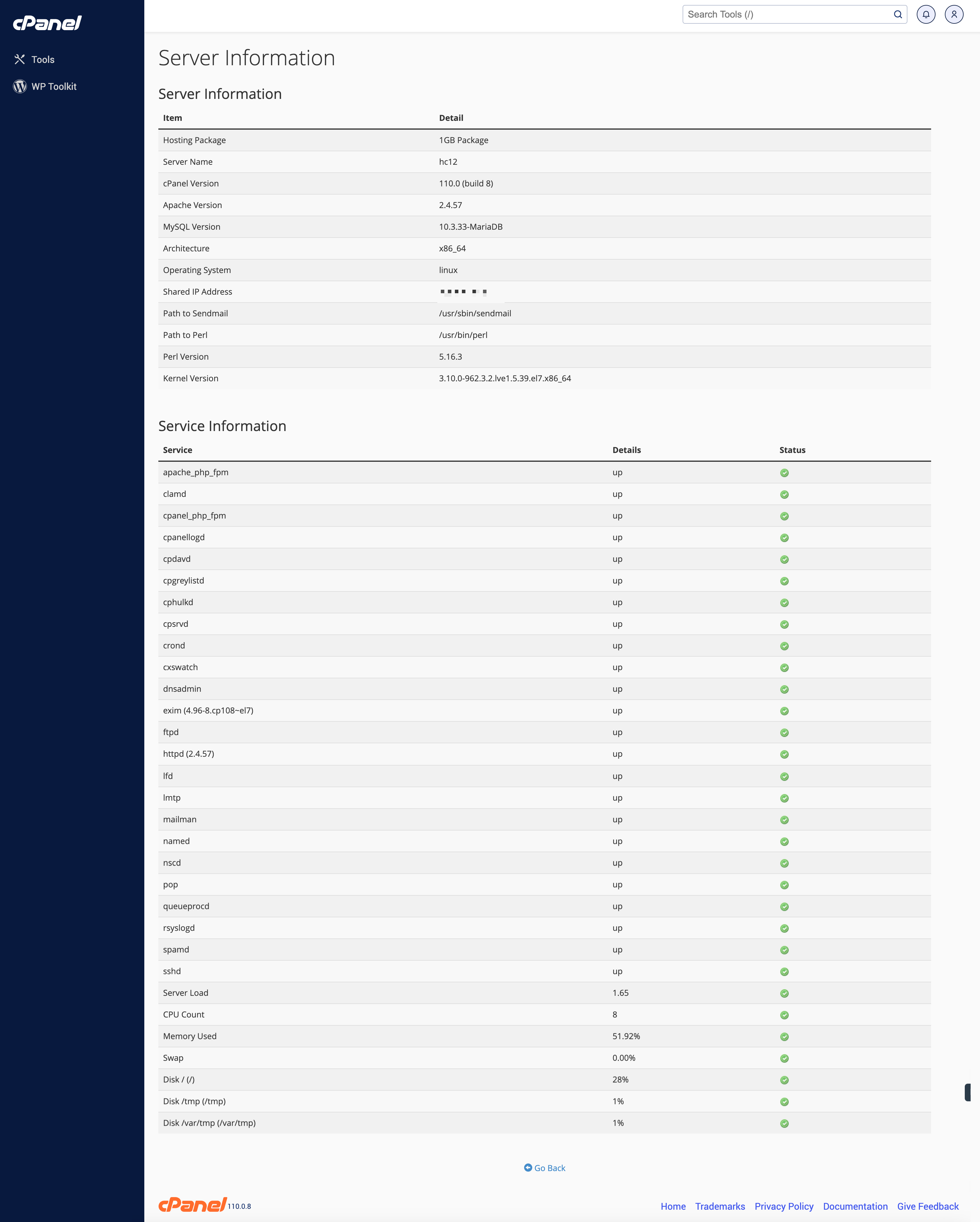
Once you click the link, the page with all the server usage information will be displayed with all the service statuses, as illustrated in Figure 12 below.
If you are using the light virtual environment of cloud Linux cPanel (as used by Batoi RAD Platform as an application sandbox and also offered to customers with low-traffic needs), navigate to Resource Usage on the cPanel main page; this option is under the Metrics section, as illustrated in Figure 13 below.
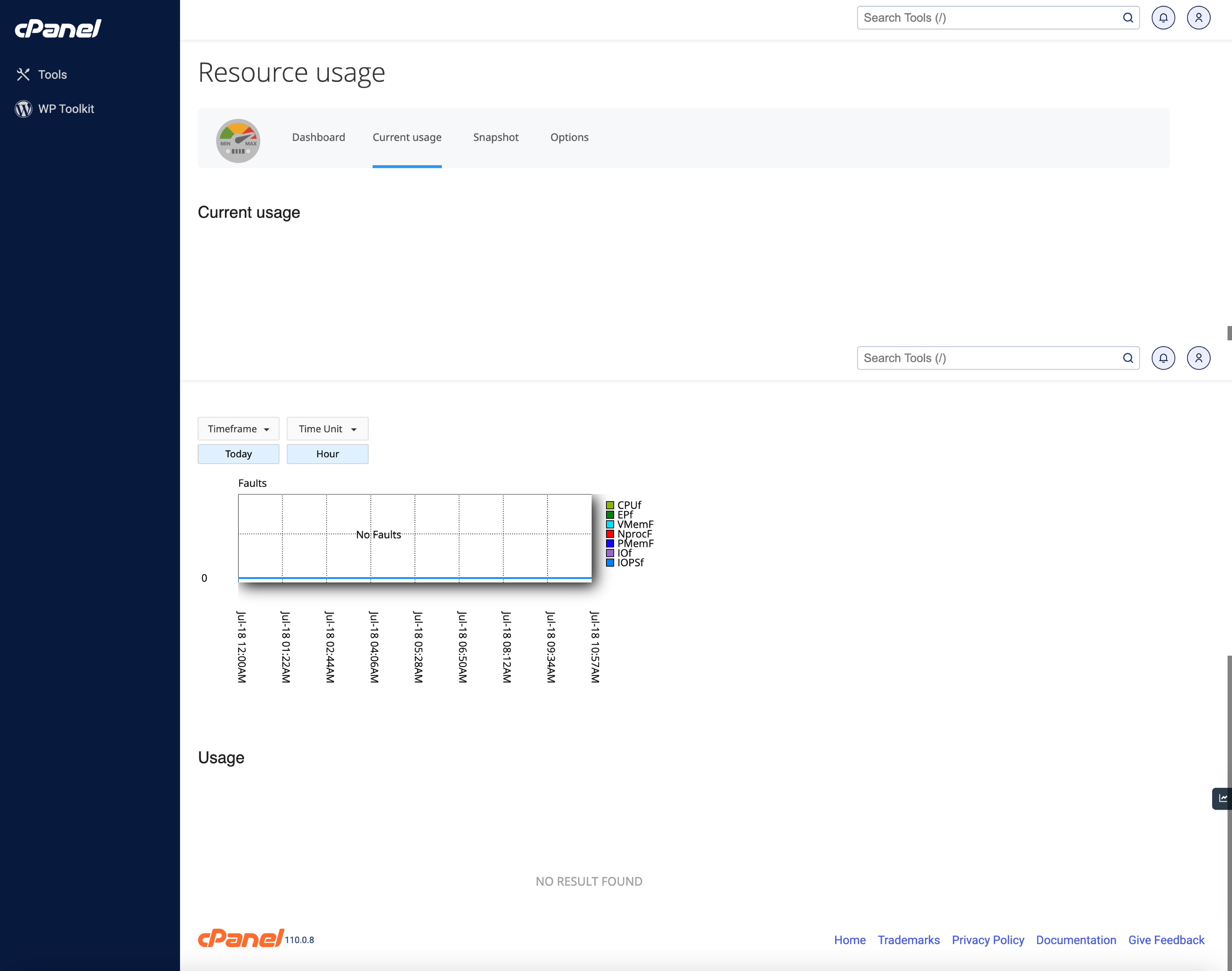
Examine CPU Usage: This tool provides a graph of your account's CPU usage and the number of connections to your website, as illustrated in Figure 14 below.
Conclusion
Regularly reviewing and managing your Linux hosting resources in cPanel can help maintain optimal website performance. If you consistently max out on your allocated resources, consider upgrading your hosting plan or optimizing your website to use fewer resources. Feel free to contact our support team if you need further assistance.