"Are we prepared for swift digitalization in the next three to five years?"
"Are we considering or understanding how today's technological investment will have cybersecurity repercussions in the future?"
Cybersecurity has always been a never-ending race, but change is speeding up.
Businesses continue to invest in technology to run their operations. They are promoting technologies into IT networks to facilitate remote work, improve the customer experience, and produce revenue that certainly exposes them to new risks.
The threat is becoming more widespread, and organizations haven’t adequate immunity. Large corporations, small and midsize businesses, and state and federal governments all confront similar risks and threats.
Many corporations realize the need to improve their cybersecurity capabilities and ensure their technology resiliency. The approach is to strengthen their cyber defenses by predicting future cyber threats as well as learning about the latest defensive capabilities that organizations may employ in the future.
Latest Cybersecurity Trends
With the digital revolution, all businesses and governments are approaching computerized systems to operate their day-to-day activities, making cybersecurity a top priority to protect data from online attacks and unauthorized access.
The top cybersecurity trends for 2022 are listed below;
Growing Threat of Ransomware
Ransomware is malware that infects computers with a virus that encrypts files and threatens to delete them unless a ransom is paid, usually in the form of an untraceable cryptocurrency. Alternatively, the software infection may jeopardize making the data public, exposing the company to massive fines.
Typically, monetization is another contributor to the surge of cyber attacks.
Cybercriminals used to struggle to benefit from attacks. Ransomware has become increasingly popular.
Cryptocurrencies and the rise of ransomware have made it easier for criminals to get away with their crimes since they can be paid in untraceable ways. This tendency has encouraged cybercriminals to commit crimes for monetary benefit while making it more difficult to track and identify them.
As a result, there is a growing demand for qualified cybersecurity specialists who can develop tactics to prevent these threats.
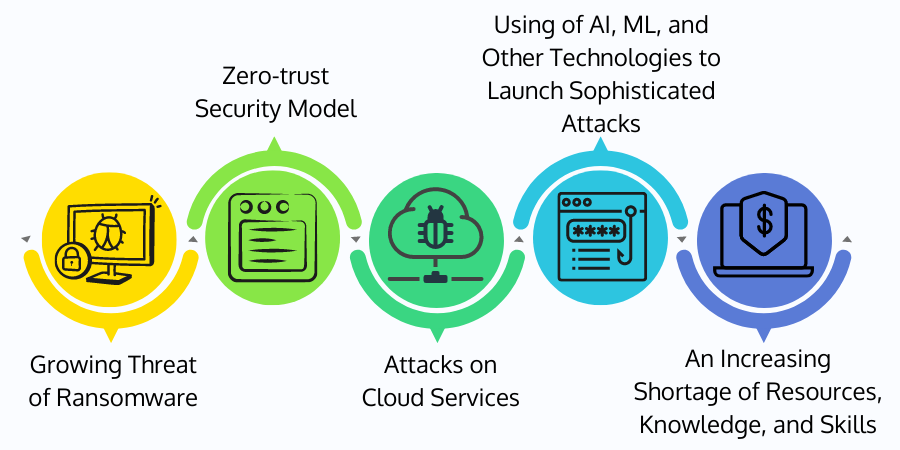
Zero-trust Security Model
As cybersecurity becomes more critical, more businesses will adopt a zero-trust network architecture (ZTNA). ZTNA is a practical security framework validating each user when they log on to the company network or LAN.
Zero-trust security model protects communications between users, devices, and programs, making it an ideal choice for remote working. Although several standards constitute 'zero trust’, NIST 800-207 can be worthy since the Biden administration enforced it for US Federal Agencies following several high-profile security incidents.
Attacks on Cloud Services
In recent years, many businesses have embraced cloud-based computing services that allow customers to access software programs, data storage, and other data services over the internet rather than depending on physical infrastructure. Cloud services have numerous advantages, including lower operating costs and better efficiency.
Although such systems can be precious to businesses, they have also become soft targets for cyber-attacks. Attackers can exploit flaws in these systems' security and obtain access to sensitive information if they are not correctly set up or maintained. This is especially essential as many modern businesses rely on cloud services where their employees work remotely.
Aside from data breaches, enterprises face the following network security trends and cloud security challenges:
- Establishing regulatory compliance across jurisdictions
- Inadequate IT competence in dealing with the cloud computing demands
- Cloud migration issues
- An increasing number of potential entry points for attackers
- Unauthorized remote access, weak passwords, insecure networks, and misuse of personal devices all contribute to insider dangers.
Using of AI, ML, and Other Technologies to Launch Sophisticated Attacks
Cyberhacking is now a multibillion-dollar industry with institutional hierarchies and R&D budgets. Cyberattackers have used advanced tools such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation.
For example, Emotet, an advanced malware that targets banks, can alter its attacking behavior. It employed potent AI and ML techniques to augment its efficacy. It used automated processes to send out contextualized phishing emails that hijacked other email threats.
Ransomware as a service and cryptocurrencies have lowered the cost of initiating ransomware attacks, which have increased every year since 2019. However, these attacks are frequently triggered by other forms of disruptions. Existing forms of ransomware and phishing are becoming more common due to new technology and capabilities.
For example, during COVID-19's initial wave, from February to March 2020, the global number of ransomware attacks increased by 148 percent. According to the report provided, from January to February 2020, phishing attacks surged by 510 percent.
An Increasing Shortage of Resources, Knowledge, and Skills
Many businesses are short on cybersecurity skills, knowledge, and expertise, and the problem is becoming worse. Cyber risk management has lagged behind the rapid growth of digital and analytics changes. Many businesses are unsure how to detect and manage digital risks.
In that response, authorities are increasing guidance on corporate cybersecurity capabilities, applying active scrutiny and focus to credit and liquidity risks in financial services as well as to operational and physical security concerns in critical infrastructure. Companies are also facing more stringent compliance obligations due to rising privacy concerns and high-profile data breaches. For instance, the White House Executive Order on Improving the Nation's Cybersecurity and the emergence of mobile-phone operating systems that ask users how they want data from each specific application to be utilized have added new data and reporting responsibilities to cybersecurity teams.
Key Takeaways
Understanding hackers' increasing intellect, behavior, and tactics can help build the best security strategies to resist threats. Cybercriminals constantly modify their practices to leverage the hybrid working culture, focusing on supply chains and network links to establish utmost disruption.
The best security practices must focus on data classification, instructing agencies to identify their most sensitive data sets and prioritize installing measures such as multi-factor authentication, encryption, and increased security logging to protect them better and migrate their apps and systems to secure cloud services.





















 Batoi Corporate Office
Batoi Corporate Office