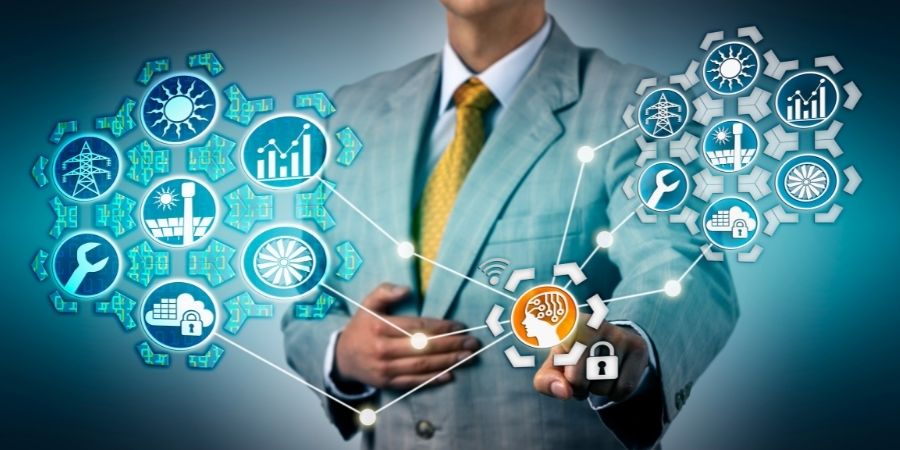

Data is the lifeblood for physical systems across all industries. However, the enormous amounts of data produced that mirrors the product life cycle are still hugely underutilized. As our assets increase in complexity and the amounts of data produced are growing, the way we need to manage and maintain them must evolve to meet these needs. A digital twin can help capture this active and passive data then represent it in a way that provides owners with current state information and predicts future outcomes.
A digital twin is a virtual counterpart, a virtual representation of physical resources, an object, or a system that spans its lifecycle. It is updated by using real-time data, using AI, machine learning, and reasoning to help in decision making, providing information on how products, nodes, and systems are currently performing and how they could perform in the future. Analysis of these data points allows us to predict failures and shortcomings well ahead of them happening. This gives organizations the ability to learn more and react faster, leading to product innovation and value creation. Simply put, a digital twin creates highly complex virtual models that are a twin of a physical thing. A physical thing could be a building, a car, a train, a bridge, or a product.
A digital twin collects data from the ‘physical thing’ through connected sensors, mapped onto the virtual counterpart ‘twin’. Then whoever has access to the digital twin can then see important information about how the physical asset works in real life.
Digital twins can help organizations to:
- Visualize products in use in real-time
- Build a digital thread and connect remote systems together
- Replicate processes to understand how they will perform
- Provide predictive analytics
- Manage system complexities
- Improve efficiency and productivity
- Troubleshoot remote equipment
Digital twins can lower the overall quality assurance and testing requirements of organizations since it doesn’t require designing and building additional physical assets. Computer simulations take this place using real-time data, which is much quicker and more cost-effective to implement. These simulations can easily integrate with the Internet of things (IoT) and Industry 4.0, AI, and data analytics software to help enhance the result. This is helping to improve performance and drive innovation.
What Challenges Can Digital Twins Solve?
Digital twins are being used across all industries, from healthcare to automotive and utility companies. Fatigue testing and efficiency improvements seem to be top of the list when it comes to solved challenges. McLaren's racing team has created virtual race cars to help give them a competitive edge by bridging the gap between the physical and virtual world. Working with real-time data from testing sessions, track days, and races provide their engineers with critical data and analytics by connecting with over 300 sensors attached to their F1 cars, equating to over 100GB of data per car. Using complex machine learning algorithms and simulations, McLaren can improve efficiency, increase performance and keep their drivers safe. McLaren has also started to implement their technology across other business areas, such as transportation and healthcare. Industries that we do not normally associate the business with.
To conclude, digital twins provide organizations with data-driven transformations, helping operators, engineers, and businesses with outcome-based decision-making. Truly a new generation of intelligence that is here to stay.
Further reading
Mclaren: How the digital twin will accelerate the fourth industrial revolution - https://www.mclaren.com/applied/blog/how-digital-twin-will-accelerate-fourth-industrial-revolution/
Forbes: 7 excellent examples of digital twin technology in practice - https://www.forbes.com/sites/bernardmarr/2019/04/23/7-amazing-examples-of-digital-twin-technology-in-practice/?sh=12f2db876443




















 Batoi Research Group
Batoi Research Group