
Unless you've been living under a rock, you've probably heard the term blockchain a lot over recent years. Google search trends for blockchain started to pick up around 2015 and are going strong today. However, the concept of a blockchain-like protocol is older than you think. Cryptographer David Chaum first proposed it in his 1982 dissertation. Things went quiet after this until 2008, when blockchain was included in the proposal for the cryptocurrency bitcoin. But what exactly is blockchain technology? What is it used for? And what are its applications in business? Let's get into it.
What is a Blockchain?
A blockchain is a digital distributed database that facilitates the recording of transactions. Information stored on a blockchain is immutable (it can't be changed) and is therefore trustworthy. But why are blockchains almost impossible to hack or manipulate? It comes down to how they work. A blockchain is essentially a digital ledger of transactions that are shared among a network of computers. In other words, blockchains are decentralized, meaning there is no one centralized source or authority that stores and validates the information.
So, how does decentralized validation work? First, each transaction is recorded as a "block" of data. Each block receives its own unique hash value based on the content of the block and the value of the previous block. So, block one is connected to block two, and block two is linked to block three, and so on.
A cryptographic hashing tool is simply a mathematical algorithm that takes a string of characters and produces a fixed-length output. For example, let's look at the hash bitcoin uses - SHA-256.
Using SHA-256, the input "Hello" becomes "185f8db32271fe25f561a6fc938b2e264306ec304eda518007d1764826381969"
Critically, changing even one character of the input string dramatically changes the resulting hash value. So, for example, if we use the input "Helli" (only one letter different to "Hello"), the output is now "196c6a941387313cfae11e55678b8e798bdde67e78a70597e18204471a0af280". It's this property of hashing that makes it immediately obvious if the blockchain has been tampered with - suddenly, the chain breaks.
Additionally, the decentralized nature of a blockchain database means that if someone tries to change the record on one instance of the database, it won't be altered elsewhere on the network. Blockchains are tamperproof.
The most well-known use of blockchains is in cryptocurrencies like bitcoin and Ethereum. However, its uses go far beyond crypto. For example, the financial sector has been identified as an industry primed for disruption by blockchain. But really, blockchain can be used by almost any sector for various purposes. You can use a blockchain anywhere you want an immutable and chronological record of transactions.
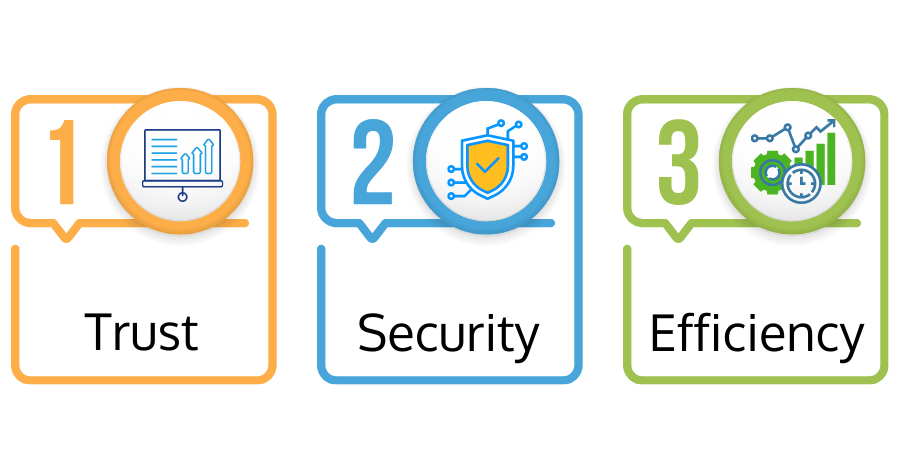
Benefits of Blockchain
- Trust - Since blockchain data can't be altered, you always have an accurate and live version of the truth.
- Security - Transactions are immutable, permanent, and validated across the whole network.
- Efficiency - Since distributed ledgers are shared among the nodes of a computer network, you eliminate all time-consuming record duplications and reconciliations.
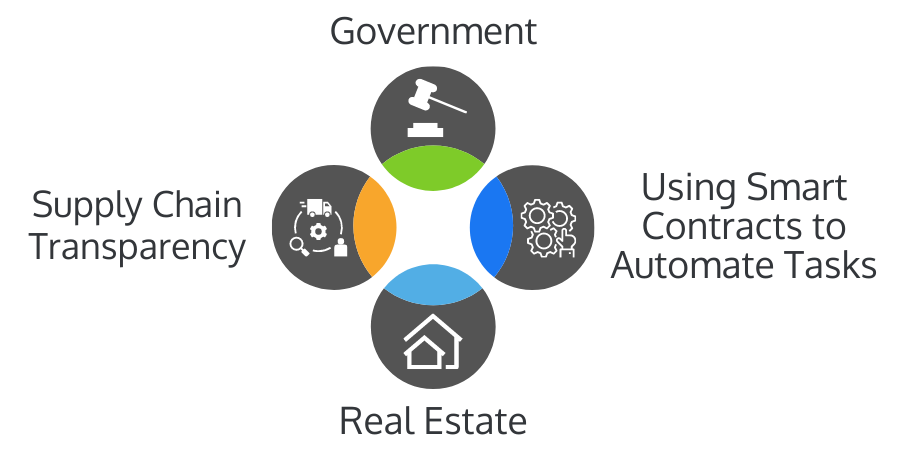
Use Cases of Blockchain
Supply Chain Transparency
Some agricultural companies are now tracking their produce from farm to table using blockchain. Using blockchains in this way became even more popular after contaminated lettuce caused many Americans to become ill in 2018, and experts struggled to find exactly where it was grown.
Beyond agriculture, many retail companies are now opting to track the source of their goods and how they move through the manufacturing cycle with blockchain ledgers.
Government
Governments can use blockchains for various activities that require a high degree of trust and security. For example, they can use a blockchain for citizen identity management, vote tracking for elections, providing an immutable record of party manifestos, and so on.
Real Estate
For most people, a house will be the most expensive purchase they make in their lifetime. As a result, having a concrete and immutable record of ownership should be a priority, and blockchain provides this.
Using Smart Contracts to Automate Tasks
Automation is a top priority in business in 2022, and with good reason. Automating manual processes dramatically reduces errors and saves valuable time and money on laborious and time-consuming tasks. Blockchains can help with automating tasks due to something called smart contracts. Smart contracts are agreements between two parties written in code and enable transactions to be executed when specific conditions are met.
The Future of Blockchain in Business and Elsewhere
As we progress through the 2020s, we can expect blockchains to become even more popular. Over the next decade, we'll see blockchain technology applied to almost all sectors in some way or another. We also expect to see medium and large-sized businesses adopting blockchain solutions at much higher rates than today.





















 Batoi Corporate Office
Batoi Corporate Office