Let us have a look at the state of security vulnerabilities today. A cybersecurity vulnerability is a flaw or weakness in your software code that attackers can exploit to gain unauthorized access to your system. When vulnerabilities go unchecked, organizations are left open to a range of threats, including malware, account takeovers, and data breaches.
The NVD database published an alarming 18000 vulnerabilities in 2020. This figure was higher than in 2019 and 2018, suggesting that vulnerabilities are rising and organizations need to be vigilant in combating them.
If we look a little deeper into the state of vulnerabilities in the 2020s, the picture becomes even more concerning. For example, one study found that 50% of internal application vulnerabilities are classified as a high or critical risk.
And if you thought that larger organizations with more resources to spend on cybersecurity fare better, then you'd be wrong. Companies with more than 100 employees see more high or critical risk vulnerabilities than their smaller-sized peers.
What is VAPT?
Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT) refers to a wide range of security assessment services designed to determine and address cyber weaknesses across a company's IT estate. It leverages the combined use of automated tools and manual penetration testing to find and exploit vulnerabilities in a target environment.
In a world where cybercriminals are always sharpening their tools and engineering novel and sophisticated ways of attacking networks, VAPT empowers organizations to stay one step ahead of the attackers. VAPT is typically performed by a third-party company to ensure impartiality.
A Quick Tour of the Different Types of VAPT
There's no one size fits all approach when it comes to VAPT. Instead, the type of vulnerability assessment or penetration testing you need will depend on several factors, including the organization's size, the kind of infrastructure, and more. In other words, every company is unique and therefore has a unique threat landscape.
Vulnerability Assessments (the VA in VAPT!)
A Vulnerability Assessment is a systematic review of the cybersecurity weaknesses in an IT estate. It determines whether the IT system (computer systems, hardware, applications, operating systems) is susceptible to known vulnerabilities or risks. A VA also prioritizes found vulnerabilities, assigns severity levels, and recommends mitigation if needed.
Penetration Testing
We can break down penetration testing based on the specific type of test (network, social engineering, application, etc.) or the amount of data the organization shares with the VAPT testers (black box, white box, or grey box).
Black Box, White Box, and Grey Box Testing
Black box, white box, and grey box are the three main categories of penetration testing, and they differ based on the level of knowledge and access granted to the third-party security team.
Black Box Testing
Black box testing is the closest to an actual hacking event. The tester isn't given information or granted internal access to the network and must obtain all the knowledge they need. The tester typically leverages open source tools and multiple hacking techniques to breach the system. While black-box testing is the most realistic and comprehensive category of pen-testing, it is also time-consuming and often comes at a high cost.
White Box Testing
In white-box testing, the pentester has all the information they need about the IT system, including network maps and credentials. While white-box testing doesn't simulate a real-world attack, it does allow the tester to conduct as many tests as possible, thereby uncovering most vulnerabilities, including those that testers could miss in black-box testing.
Grey Box Testing
Grey-box testing strikes a balance between white and black box testing. Essentially, the testers are given limited access and information like the IP address of the target and some lower-level credentials. Grey-box testing simulates an attack where the hacker has already penetrated the perimeter. It also highlights the potential damage of an insider attack.
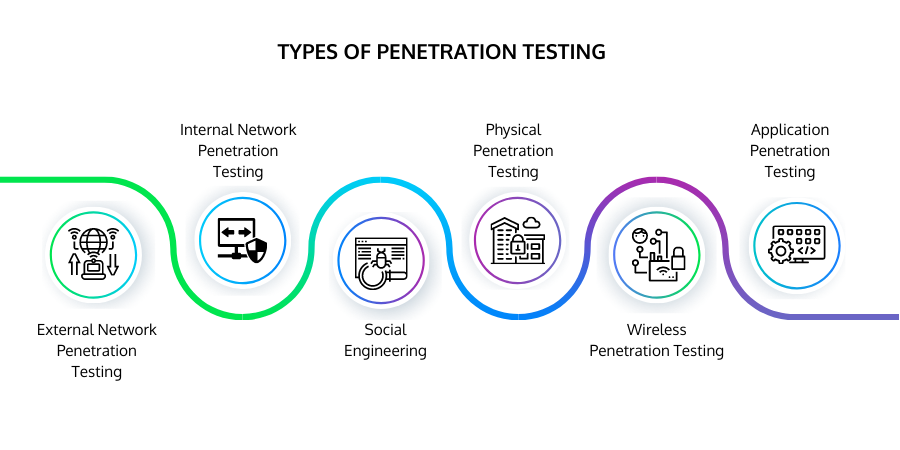
The 6 Main Types of Penetration Testing
There are six main types of specific penetration testing, and these are:
- External Network Penetration Testing - Testers use publicly available information or external-facing assets like cloud-based applications, websites, and company emails, to attempt to gain access.
- Internal Network Penetration Testing - Assesses the organization's vulnerability to insider attacks from rogue employees or third parties with access to the internal network. It looks at elements like network traffic, secure passwords, patching, authentication, encryption, network configurations, and information leakage.
- Social Engineering - Assesses how susceptible employees are to handing over privileged information that can be exploited in an attack. For example, the hacker might pose as a trusted individual or entity and attempt to trick the employee into sharing sensitive data or carrying out a dangerous act, like downloading malware.
- Physical Penetration Testing - Simulates a physical security breach where an unauthorized party gains access to the building, office, or data center. Assessors pose as trusted individuals or use other methods to circumvent security protocols.
- Wireless Penetration Testing - Identifying and evaluating the connections between all devices on the organization's WiFi.
- Application Penetration Testing - Focuses on finding vulnerabilities in the design, development, and implementation of the organizations' applications.
VAPT as a Cyber Defense
It's more cost-effective to prepare for a cyber attack than wait until one happens. Cyber attacks and data breaches incur considerable costs to organizations, both in financial losses and reputational damage (clients don't want to work with companies who can't protect their data and systems). With this in mind, VAPT is the perfect method of cyber defense.
Benefits of VAPT
- Detailed overview of potential threats - You can only mitigate the threats you are aware of, so a detailed overview of all threats is paramount to protecting your IT estate.
- It helps uncover misconfigurations in applications - Human error is the number one cause of data breaches. Patching vulnerable, misconfigured code or end-points is essential to robust security.
- It helps mitigate critical vulnerabilities and prioritize risks - VAPT can tell you which vulnerabilities present the most significant threat to your company and need fixing first.
- It helps discover gaps between security tools - A single tool won't uncover all vulnerabilities. Since VAPT uses a comprehensive approach to security, utilizing automated tools and manual methods, you can discover the gaps between tools.
- It helps safeguard the company from costly reputation and revenue losses. After mitigating the vulnerabilities found in VAPT assessments, your company is less likely to fall victim to a successful cyber attack.
Next Steps
Cybersecurity vulnerabilities present a significant risk to organizations today and in the future. The best way to safeguard your IT estate from cyber attacks is to take a deliberate and systematic approach to cybersecurity. VAPT assessments are a critical part of this, following cybersecurity best practices.
Additionally, you can protect your IT systems by building new applications with security in mind from the get-go. Antiquated technology is a crucial reason for vulnerabilities in many organizations. Therefore, we recommend moving away from old technology and outdated frameworks to more comprehensive and robust alternatives. For example, Batoi RAD Framework, a LAMP stack application framework, adheres to the latest security controls and criteria. Equipped with Batoi RAD Platform, organizations can create the next generation of apps and services in the cloud, supports ultra-fast app development, live code editing, and more, all while ensuring state-of-the-art security.

 Batoi Corporate Office
Batoi Corporate Office