Your modern data stack is the essence of your core analytics architecture.
A modern data stack is a platter of tools and technologies to render, employ, and manage data for analytics. Its core aspects are data workflows, data management, analytics, and querying. Effective modern data stacks are business-critical while enabling businesses to adopt analytics more widely, and use data more frequently. On the other hand, ineffective data stacks can restrict an organization's ability to use data effectively, resulting in additional technology expenses.
Having that, let's examine what a modern data stack looks like and the major aspects components, characteristics, and benefits.
What is a Data Stack?
A data stack is a collection of tools or technologies used to assemble, clean, save, and transform data.
These solutions give data engineers and analysts the ability to
-
Collect and organize data in one location,
-
Transform unprocessed data into useful information,
-
Store data at the preferred location, and
-
Analyze it as required.
A data stack aims to process, clean, and analyze data as, without such steps, data is meaningless.
Discussing Modern Data Stack
Data stack and "modern data stack" are frequently used interchangeably. The sole distinction is that a modern data stack uses innovative, modern solutions running on cloud-based data warehouses.
Dissimilar to legacy data stacks, modern data stacks are located in the cloud and are more accessible and scalable. They help address the data management issues that conventional data stacks cannot resolve.
Transitioning From ETL to ELT
Before developing cloud solutions, data processing and management worked differently. The standard data stack structure was heavily based on extracting, transforming, and loading (ETL) method. This process entailed accumulating data from distinct sources, transforming it t polish it for storage, and then loading it into the database.
Conversely, a modern data analytics stack reverses the steps in the extraction, loading, and transformation process (ELT). Using ELT, organizations can load data into warehouses without first transforming it. This approach runs many benefits over the outdated ETL approach, such as increased data usability, improved data analytics, and cost-effectiveness.
Modern Data Stack Benefits
A modern data stack has many advantages aside from significantly lowering the technical barrier to stepping in.
-
First, modern data stacks are built to keep business users into account. Modern cloud architecture can eliminate multiple vendor lock-ins, eradicate data silos, and integrate everything into a centralized data warehouse.
-
Second, SaaS tools are more scalable and cost-efficient. Businesses can opt for pay-as-you-model and on-demand, scaling resources up or down in real-time. The best part is there is no need to provide hardware and forecast usage over time.
-
Third, data engineering and analytics professionals can save a substantial amount of time by utilizing pre-built interfaces. They can now focus on generating business results.
Legacy Data Stack vs. Modern Data Stack
The prime difference between conventional and modern data stacks is on-premise hardware and cloud-native tools and technologies. Legacy data stacks run on-prem that must be deployed, managed, and scaled separately as the business vertical evolves or shifts.
Cloud and SaaS-based products free up users with extra pressure so they can invest their efforts in achieving business results rather than technology. By contrast, modern data stacks are cloud-hosted, meaning all the hardware-related management and maintenance are handled automatically as a service. As users can avail of “pay for usage”, they are not required to purchase the underlying resources, making modern data stacks cost-effective.
Modern Data Stack Components
Since a modern data stack facilitates data flow from sources to analytics and data science tools, it is easy to think of a data stack as a linear set of tools. It is more appropriate to think of a modern data stack as a sphere of technology components with one major component at the center – a cloud data warehouse. There are many components that you can integrate into your modern data stack. Sometimes, you might use multiple tools in a category (i.e., BI and Analytics tools). Below we define a core modern data stack essential for a successful data stack and then identify some additional tools.
It is appropriate to portray a modern data stack as a province of technology elements with a cloud data warehouse - as its central element. Users can combine various elements/tools into their modern data stack. The basic modern data stack is made up of the following components:
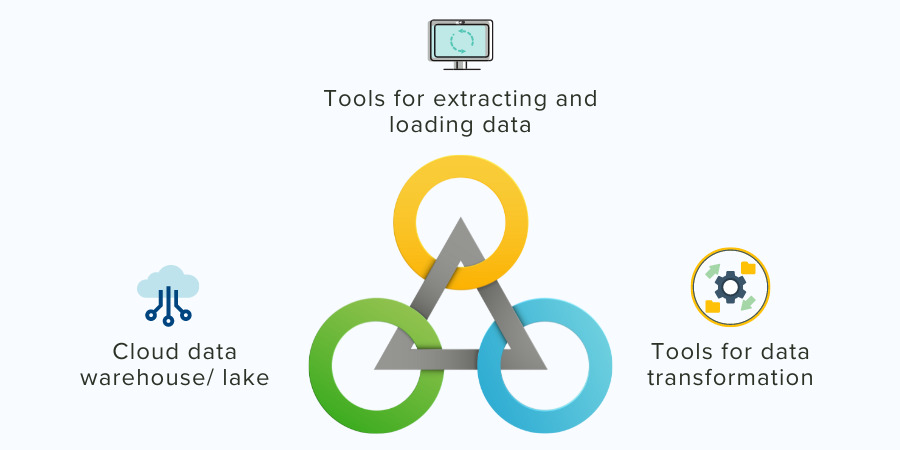
Core Modern Data Stack
The core modern data stack consists following tools/platforms:
-
Cloud data warehouse/ lake: This provides data management, processing, and storage in a modern data stack.
-
Tools for extracting and loading data: These help provide EL (Extract and Load) data into the cloud data warehouse.
-
Tools for data transformation: Once data is uploaded in the warehouse, these tools convert your raw data into definite data analytics models.
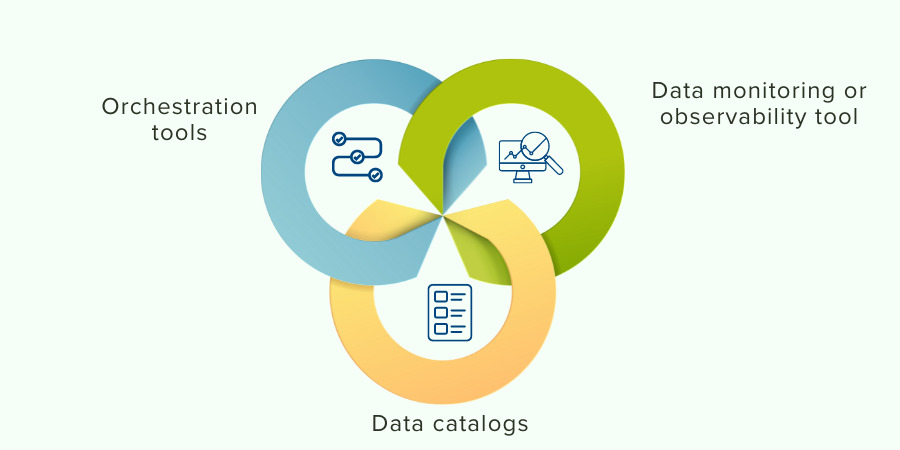
Additional Data Stack Tools
Additional tools consist of:
-
Orchestration tools: These help organize data pipelines that offer several tools in your data stack, such as workflows, including both EL and data transformation tools.
-
Data catalogs: These tools support building a data asset inventory, team dataset discovery, and data governance.
-
Data monitoring or observability tools: These assist users in examining how data pipelines function and tracing the overall data activities.
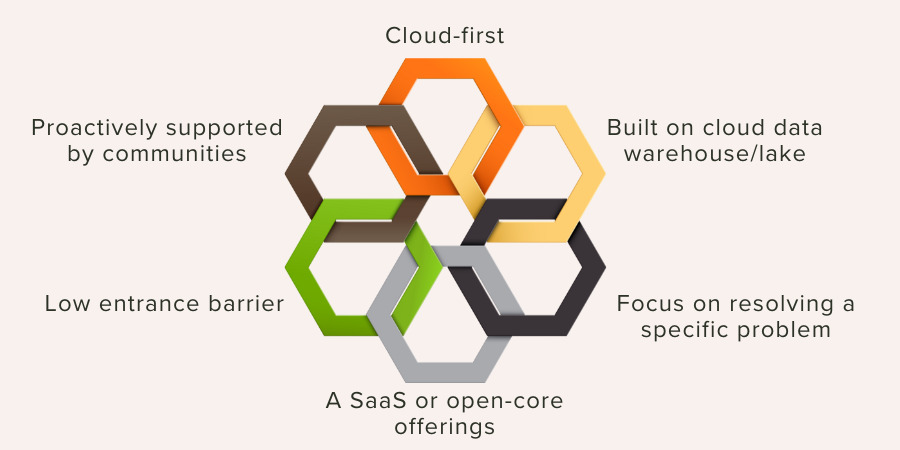
6 Characteristics of Modern Data Stack
Cloud-first
Modern data stack tools are highly scalable and flexible, thanks to modern public cloud vendors. This enables businesses to incorporate existing processes with cloud infrastructure.
Built on Cloud Data Warehouse/lake
Modern data stack tools realize that a central cloud data warehouse or lake expedites data analytics at scale. They can easily be integrated with all popular cloud data warehouses such as Redshift, Bigquery, Snowflake, and Databricks and be fully used at best.
Focus on Resolving a Specific Problem
Modern data stack connects various phases of data pipelines to fully leverage each tool focusing on data processing or management. This also enables modern data stack tools to be best suited to disparate cloud architectures with minimal changes to existing stacks.
A SaaS or Open-core Offerings
Most modern data stack tools are SaaS-based. However, the basic elements are open-source In some instances and include premium add-on features such as end-to-end cloud hosting and expert guidance.
Low Entrance Barrier
Today's data stack products come with pay-as-you-go and usage-based pricing structures. Before making significant investments, data experts must evaluate new technologies, features, and usage. Modern data stacks are built on low-code/no-code platforms. Installing and setting up a tool only takes a few hours and doesn't require a lot of technical know-how.
Proactively Supported by Communities
Modern data stack solutions providers devote ample time and energy to community development. Many slack groups, meetings, and conferences actively support users, data practitioners, and tools. This encourages creative and supportive ecosystems around these tools.
Conclusion
A modern data stack is a lot of planning and technological research. Enterprises can swiftly adopt analytics if a robust modern data stack is in place. Conversely, an ineffective data stack could result in additional expenses for the data engineering and technology side.
Implementing a structured method to build a modern data stack is viable. The result will be an efficient use of cloud resources at reduced costs, faster analytics projects, and higher analytics adoption within organizations.





















 Batoi Corporate Office
Batoi Corporate Office